What’s the difference between superfast & ultrafast broadband?
Posted on 6 August 2021 by Beaming SupportThere are two types of fibre broadband. You may know FTTC or SOGEA as superfast broadband, fibre broadband or “traditional” fibre broadband, while FTTP is sometimes called ultrafast broadband, full fibre broadband.
As a user, the main differences you’ll notice between superfast and ultrafast broadband are that:
- Ultrafast broadband provides faster speeds than superfast broadband
- Ultrafast broadband usually costs more than superfast broadband
As an internet service provider for businesses, we help companies make informed decisions about their connectivity needs, so we won’t just leave it at that. In this article we’ll give an overview and detailed explanation of the differences between SOGEA and FTTP broadband so that you can choose the right technology for your business purposes.
At a glance – the difference between superfast and ultrafast broadband
| SOGEA | FTTP | |
| Best for |
|
|
| Type of line | Fibre optic to the local cabinet, then copper to the premises
(Broadband only service, no voice service attached) |
Fibre optic
(Broadband only service, no voice service attached) |
| Uncontended (your own dedicated line) | No | No |
| Installation lead time |
|
|
| Repair time (Service Level Agreement) |
|
|
| Contract minimum |
|
|
| Data usage | 100GB or unlimited usage packages available | Unlimited |
| Connection charges |
|
|
| Business applications |
|
|
What’s the difference between superfast and ultrafast broadband?
Fibre broadband – both superfast and ultrafast – gets its name from the technology used to deliver data at the speed of light through fibre optic cables, but only with FTTP does data travel its entire journey through fibre optic cables. This is explained and illustrated below.
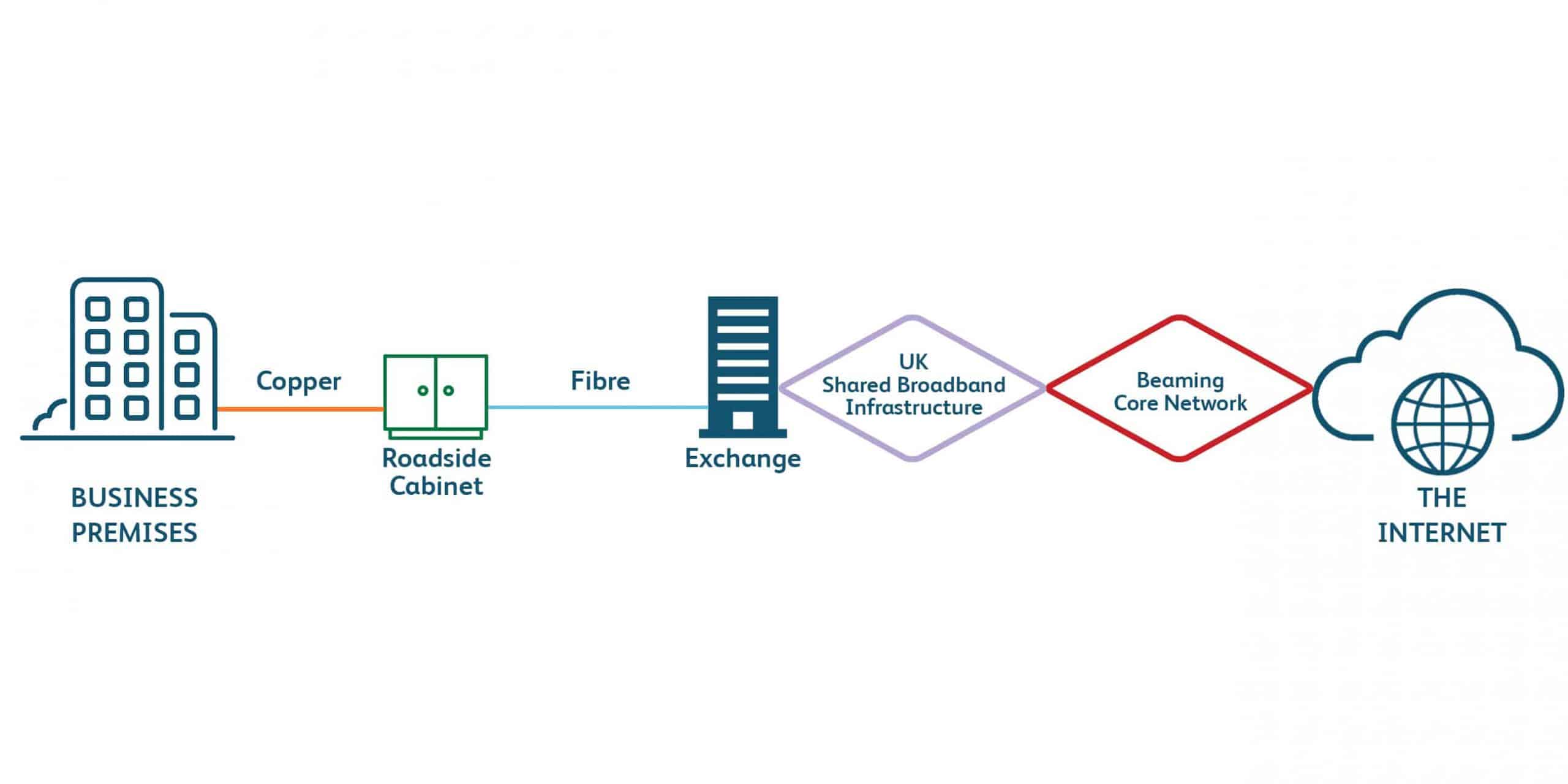
SOGEA Broadband (Single Order Generic Ethernet Access)
Also known as: Superfast fibre broadband, a broadband only service that does not have an associated telephone line for voice sevices
How SOGEA connects businesses to the internet:
- Fibre is delivered to the green cabinet (PCP – primary cross-connection point) and then copper is delivered to the DP (distribution point) and into the premises.
- Can be delivered via underground duct or copper wires from telephone poles.
- Uses the BT Wholesale broadband network (shared bandwidth) with multiple points of failure and asynchronous bandwidth (higher download than upload).
Speeds:
- Speeds will vary depending on the length of the copper line from the green cabinet.
What would you use it for?
General email and browsing
- VOIP & cloud for smaller businesses
Installation:
- The service does not include a telephone line or number.
- Requires a broadband router connected to the installed socket.
- Lead time is usually within 2 weeks from point of order.
- The service can be migrated to another provider.
Service Levels:
- Fix time SLA – standard 2 working days repair for the broadband, different service levels available for the PSTN line.
GET MORE INFORMATION ABOUT FTTC FROM BEAMING
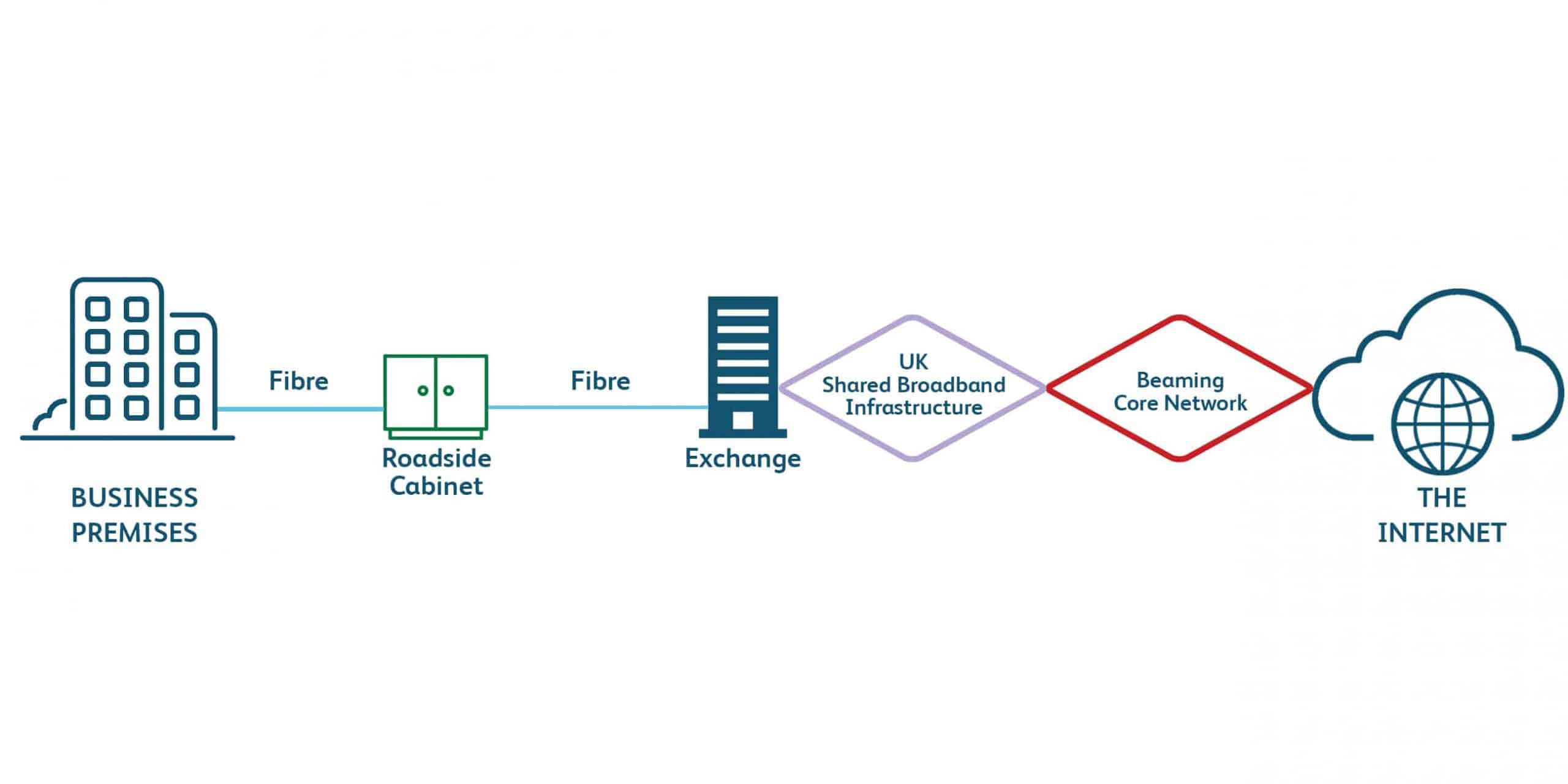
FTTP – Fibre to the Premises
Also known as: Ultrafast, Fibre to the Home (FTTH), next gen fibre broadband.
How FTTP connects businesses to the internet:
- Fibre to the office from the nearest green cabinet.
- Can be delivered underground in ducts or overhead from poles.
- Uses the BT Wholesale broadband network (shared bandwidth) with multiple points of failure and asynchronous bandwidth (higher download than upload).
- There is no associated PSTN line rental and the router needs to support PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet) on the WAN interface. The router is connected to the Openreach supplied Optical Network Termination (ONT) device.
Installation:
- Requires a broadband router connected to the installed socket.
- Lead time is usually within 10 working days from point of order (if FTTP is available at the location).
- The service can be migrated to another provider.
- The service does not include a telephone line or number.
Speeds:
- Comes in different speeds for cost reasons but not dependent on line length and the speed can be upgraded.
What would you use it for?
- Small business processes that require higher bandwidth such as sharing large files or collaborating online
- General email and browsing
- VOIP & cloud for smaller businesses
Service Levels:
- Fix time – standard 2 working days.
GET MORE INFORMATION ABOUT FTTP FROM BEAMING
Find out more about FTTP:
Can I upgrade to Ultrafast broadband?
I can’t get FTTP in my area, what can I do?
Should businesses upgrade to FTTP?
How much should I spend on business broadband?
If you think your requirements exceed what’s offered by fibre broadband, have a look at these articles which compare more fibre optic connectivity:
- What’s the difference between FTTP and a fibre leased line?
- What’s the difference between internet fibre leased lines and point to point fibre?
Get more information or a quote
Beaming’s team are experts in connectivity and networking, so they can help you choose the right connection for your business. Use the form below or call us on 0800 082 2868 to get advice tailored to your requirements.
Businesses that benefit from Beaming broadband

- Hosted Voice
- Telephony
- SME
Abbotprint
An ageing ISDN telephone system and a desire to be prepared for the future prompted the move to cloud voice technology for this innovative printing firm.

- Education
- FTTC
- Broadband
- WiFi
Artemis Nurseries
Aiming for a paperless system, Artemis’s director, Emma Buggy, needed the right infrastructure to support this new technology.

- Broadband
- FTTC
- Not For Profit
East Grinstead Museum
With exhibits including stories of worldwide importance – in particular that of the East Grinstead Guinea Pig Club – internet connectivity is an important part of improving and maintaining the accessibility of the museum’s collections.

- Data Security
- Digital Transformation
- Broadband
- SME
Old Hastings House
The team at Old Hastings House care home found it paid to find a partner who put their needs first.

- Remote Working
- Broadband
PR Artistry
PR Artistry is a PR and content creation company. Since 2017 everyone at PRA has worked remotely therefore a central point for the company’s connectivity & communication is essential.

- Broadband
- Remote Working
The Adastral Group
With one eye always on the future, the Adastral Group knew there was likely to be a move towards the virtual delivery of training, but they couldn’t have predicted quite how quickly this would happen.